|
QuickFind Page Index
|
INTRODUCING THE LEARNING STATIONTM
Summerland presents products and a facilitating system
program for integration of student use computers in classroom and home
environments. Because the successful brand development of Summerland's
Learning Station is dependent on both public and private sector support
and acceptance, particular attention has been given to our being able
to anticipate and accommodate requests and responses from educators,
regulatory agencies and public interest groups. Our strategic plan is
to provide economically justified computer workstation desks; to aid
both school and home decision makers to responsibly acquire and manage
education use computers, and to be able to communicate solutions to
cost and use concerns.
| Every citizen of the US, and of the world,
recognizes the vital impact of maximizing quality of student training
to national and individual student development. The ability of schools
to develop future leaders is based on every citizen having complete
confidence that responsible utilization of technology is a functional
part of education's' operational protocols. Each component of Summerland's
educational products, and systems for their use, must be structured
to earn and honor that trust. Our approach has to accommodate a
wide range of resource use planning action alternatives. |
Background
US and international programs are in place to stimulate
expanding use of computers in schools and for students use at home.
US Funding (federal) to establish internet links to every school
and (state and local) programs for provision of
in-class room computers facilitate implementation of new computer teaching
protocols. Summerland's approach is to assist decision makers to reach
workable decisions - - making certain that computer use is programmed
with broad consideration of economic and educational options.
|
Summerland's patented, ergonomically responsible, mobile
Learning Station ™
adjusts to meet specialized requirements of growing students from K-12 and
beyond. Computer assisted learning melded with the Student Learning Station's
functional workspace is a practical system solution for education and training.
Top - Page Index
|
We believe that interfacing even very young
students with computers; giving them access to the Internet and using
the computer as a major part of day-to-day educational instruction, is
the most efficient method for obtaining exemplary educational results
- - at the lowest cost.
Every child in every classroom should have access
to a computer. We think that homework should routinely involve working
with information sources on the Web and, we think it all should be accomplished
as rapidly as possibly.
|
COMPUTER ASSISTED TEACHING
YIELDS STARTLING RATES
OF STUDENT DEVELOPMENT
Test results prove it. Students that utilize computers in
school and at home acquire "learning-how-to-learn" skills faster than
their non computer aided contemporaries. Computers present traditional text
book information in an interactive format that facilitates knowledge absorbing.
Students working on a computer feel more free to ask questions and receive/understand
answers in a non-competitive, individual atmosphere. Computer aided students
learn faster and retain more information better in the classroom and at home.
Computer using student learning improvement is affected by two non hardware-software
factors:
- THE AMOUNT OF TIME A STUDENT IS ENABLED TO WORK ON A COMPUTER. Every
computer user discovers how important it is to use the same computer as opposed
to a variety of different units. Computers, like automobiles, have individual
quirks - - it takes time to develop facility with any machine. It takes extended
periods of utilization to make a computer into a fully developed individual's
learning aid. When computers are centralized in computer labs because of lower
initial costs, limited student access inhibits development of a computer-student
interrelationship.
- THE STUDENT'S COMPUTER WORKING AREA CONFIGURATION. Computers introduced
into a classroom without an idealized enclosure are subject to damage to hardware
and student. Without proper room lighting, support seating and keyboard and
monitor adjusted to correct positions, highest learning productivity rates
are not able to be achieved; physical injuries including carpal tunnel syndrome
result and even the best developed teaching programs are jeopardized.
|
Horror stories abound. - - for example:one fourth grade
class played bumper-cars with their rolling computer carts - - a computer
aided middle school health class was enlivened by students' slipping adult
CDs into the classroom server - - three monitors were broken by
baseball bat accidents in a sixth grade classroom - - multiple instances
of discoveries of asbestos during hard-wiring installations resulting
in school room hard wiring costs in excess of $15,000 per classroom.
|
The Student Learning Station space and desk/enclosure
layout design center around optimizing placement of the monitor display, its
controlling keyboard and mouse. Critical considerations are positioning
of the display relative to desk top work surface; providing mechanical protection
of the monitor and CPU from damage, and sizing and arrangement of the work station
desk top to allow adequate space for regular desk use. During computing, user
performance is enhanced and fatigue reduced because monitor height and view
angle changes can readily be adjusted at regular intervals. Top
- Page Index
Starting at the beginning . . .
Elementary school-age children grow rapidly - - significant
growth occurring during a school year. We addressed the elementary school student's
needs for a work station that fits - - and grows as the child grows. The
OFFICE™ Student Learning Stationtm
features desk unit mobility plus the capability of use as both a computer work
station and conventional writing desk. It is an economical, ergonomic, mobile,
combination computer workstation and desk unit for school, classroom, or home
use that permits adjustment of monitor and desk top height.

Typical primary classroom with damage susceptible hardware
The
Learning Station™
replaces traditional student desks.
The combination desk top and monitor lift permits the unit
to work as both a computer workstation and conventional desk. Key switch
controlled monitor raising/lowering is accomplished electrically. Monitor height
positioning is to be able to be accomplished by the student (does not require
intervention, tools or assistance).
The Learning Station monitor lift system has two functions:
- (1) to permit the computer monitor to be automated for its removal
from a desk top or task area in order that a user has a clear work surface,
and to provide security for computer equipment; and,
- (2) during computer use, to facilitate positioning and repositioning
a monitor to achieve an ergonomically correct, optimal, viewing height
and to be able to vary that height during a work session.
|
The monitor lift is an economical, electrically
powered system with controls. It is quiet, reliable and handles a wide range
of monitor sizes and weights. Its in use operation requires only pushing control
buttons. Key switch and button are in an OSHA safety switch configuration
(requires two-hand operation).
Safety features: Lift design provides that during
monitor movement, operator fingers are not able to be inserted into a position
where damage might occur. Edge and corner protection has been incorporated so
there will be little danger of tripping over any parts of the units or striking
against projecting parts during both normal use and general class room activities.
Guards, frames and other structural components are robust to prevent the possibility
of their giving way and permitting an accident in the event a user should fall
or be thrown against them.
The lifted top provides a smooth writing surface when the
computer is in its stowed position. The monitor, CPU, keyboard and mouse are
contained within the lift unit. They all rise and lower as a unit - - with extraordinary
safety features in place. The unit incorporates network cable or wireless antenna.
Options include telephone/internet connectors. Only a single power cord input
is required. The lift mechanism operates at low voltage (12 v. DC). Top
- Page Index

|
 |
|
Viewing Angle adjusts
|
Height adjusts to fit
Shown above is K-4 model for younger students,
typically from Kindergarten through 4th grade
|
- K-4 Desk height is adjustable so that the desk top can be moved
over a 5" - 7 " height range.
- For the smaller child, the desk top is positioned at the lowered
height.
- Keyboard and mouse are used on a stable work surface platform at
varying heights. Left or Right hand use by reversing writing/keyboard
platform!
- Lift raising/lowering provides "fine" up and down height
adjustment control so that the monitor can be accurately positioned
to within one-half inch without "drifting" when the height
adjustment control is released .
|
|
Model LS-512
for 4th
and 5th grades through University students & adults.
Laminate finish. Cabinet doors are optional. Accepts up to a 21"
monitor and 19" CPU tower.
CONVERTS at the touch of a switch from adjustable
desk to adjustable computer workstation.
IN DESK POSITION:
Desktop
slides --forward-- > to provide maximum leg room and work
comfort.
Desktop infinitely adjustable: Adjusts UP and down from 28"
to 45" table height.
IN COMPUTING POSITION:
Monitor
and keyboard height are adjustable
Adjustable monitor height feature ensures unobstructed line of sight
to instructor
- Maximum ergonomic flexibility.
- Computer disappears to
clear desk for non-computing tasks at the touch of a switch.
- Rounded corners, safety functions, no places
to pinch little fingers
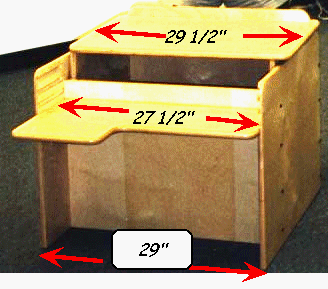
Dimensions & Travel Range:
28" wide* x 24" deep x 28" h (desk top lowered position)
Adjustable inset Desk Top measures 26"w x 24" deep with
forward slide travel of 17"
Desktop infinitely height adjustable from base of 28" to a 45"
table height
*Cabinetry Dimensions add 1 ˝" each side for wheels located at
rear of unit.
TOUCH
THE SWITCH - The LS-512 model CONVERTS FROM ADJUSTABLE DESK
WITH PULL-FORWARD TASK AREA DESIGNED FOR MAXIMUM WORK COMFORT,
TO AN ADJUSTABLE COMPUTER WORKSTATION

VIEW MORE: LS-512 model PHOTOS
Also Specifications for LS-512
|
 |
|
SCHOOL APPLICATIONS
The Student Learning Station, as replacement for conventional
classroom desks and tables, is a critical component in an "ergonomic computerized
classroom system" (see below for one way in which it works).
As an integration of computer workstation and conventional desk, it replaces
traditional student desks. Selection will be predicated on blending function/cost/size
to permit large numbers of units to be employed per classroom.
Computers in classrooms change how students perform their
tasks. Classes may be divided into multiple groups, simultaneously studying
different subjects. The groups may change during every school day. Part of each
study most likely entails both computing and non computing tasks. Top
- Page Index
We have addressed the student’s needs for a work station that
fits - - and grows as the child grows. Elementary school-age children grow rapidly
- - during the school year. In order for them to have an effective working position
that takes into account ergonomic needs, the units are designed to adjust to
fit the widest possible student size-range. The OFFICE™ that Grows features
integrate mobility of the Student Learning Station desk unit plus its capability
for use as both a computer work station and conventional writing desk.
· Desk mobility is provided with lift and roll units that when in the "raised"
position, permit the desk to be freely moved. But, when lowered, the unit is
securely sited.
· The monitor is able to be lowered from the desk top to an out-of-the-way
position by the student. The desk top height can be adjusted over a range to
accommodate growth.
· Unit construction is designed to take the wear and tear expected from students.
The monitor is shielded from damage when in its lowered position. All moving
parts are within the "guard" area. Drive limit switches provide maximum upper
and lower height limits. Top - Page Index
 Power for the monitor lift is provided through an internally mounted, sealed
gel-cel battery with installed trickle-charger. All wiring is in accordance
with high-duty standards for maximum reliability. Monitor raising and lowering
is controlled via a spring-loaded rocker switch requiring holding in its energized
position to effect movement. The circuitry provides for required holding of
a second normally-off switch in its energized position so that both user hands
are required to raise or lower. The monitor lift has an internal electrical
lock such that there is no "slip" downwards. The lock feature holds in excess
of 100kG.
Power for the monitor lift is provided through an internally mounted, sealed
gel-cel battery with installed trickle-charger. All wiring is in accordance
with high-duty standards for maximum reliability. Monitor raising and lowering
is controlled via a spring-loaded rocker switch requiring holding in its energized
position to effect movement. The circuitry provides for required holding of
a second normally-off switch in its energized position so that both user hands
are required to raise or lower. The monitor lift has an internal electrical
lock such that there is no "slip" downwards. The lock feature holds in excess
of 100kG.
OPERATING REQUIREMENTS & INSTRUCTIONS
- Remove Packing and insert keyboard tray.
- Position Unit
- Pass 110v pigtail from surge-protection strip through exit at rear of unit
& connect to grounded wall outlet
- Turn "on" switch on surge protection strip - switch light comes on
- Verify that charger lamp (red) is lit
TO INSTALL COMPUTER HARDWARE IN UNIT:
- Install CPU
- Connect keyboard cable to CPU.
- Connect Mouse to CPU
- Connect CPU - Monitor connecting cable to CPU
- Connect CPU Power cable from CPU to surge strip outlet
- Place Monitor on Monitor Platform & connect CPU-Monitor Cable
- Connect Monitor Power Cord to surge strip outlet
- Turn Strip outlet switch to "on"
To Operate Unit
- Hold RIGHT side toggle and simultaneously push rocker switch "up"
to raise or "down" to lower monitor.
- Position Monitor for best viewing height
- Adjust keyboard/writing surface by selecting proper height slot
DESIGNED TO LAST (normal classroom usage)
- Lift Mechanisms warranty - - five years
- Lift Motor - - 50,000 cycles
- Cabinetry warranty 1 year (High-Pressure Laminate finish units 3 years)
Cabinetry Material Design Notes
The cabinetry materials selected represent a major forward step in furniture design.
The composite material combines outstanding strength with near-total resistance
to warpage and moisture at heretofore not attainable light weight. Far stronger
than particle board, the cabinetry is designed to take the bumps and bruises of
daily use. The cabinetry material is environmentally beneficial too - - excepting
for the high-pressure laminate surface material(s), - - it is fully biodegradable.
Cabinetry incorporates structural components and wiring and fasteners
internally .
This space-age design provides reliability advantages over other materials.
It means that no wiring or mechanical fasteners are exposed to damage. From
a manufacturing perspective, assembly of units is more workmanship error-free
because component sub-assemblies are quality and reliability control tested
for workmanship electrical and mechanical function as individual parts. For
speed in delivery and maintenance of the lowest possible costs, units can be
rapidly built-up on a just-in-time basis and shipping costs are substantially
reduced because of the light weight. Design diagrams. (1)
- (2)
Top - Page Index
With the Student Learning Station . . .
- Desk mobility is provided with lift and roll units that when in
the "raised" position, permit the desk to be freely moved.
But, when lowered, the unit is securely sited.
- The monitor is able to be lowered from the desk top to an out-of-the-way
position. The desk top height can be adjusted over a range to accommodate
growth.
- Student Learning Station construction is designed to take
wear and tear, work very well, and last a long time.
|
Tomorrow's classroom will, at nearly any point in time, have
students working on computers and others occupied handwriting, reading or other
non computer using tasks. Envisioning the future in this way is only constrained
by budget limitations.
The Summerland Student Learning Station provides computer-age
benefits at costs expected for today's outdated student desks.Top
- Page Index
At Home
The computer and the Internet provide unmatched learning
opportunities. Students who are able to develop computer facility at the earliest
possible age are best equipped to learn. Student computer stations in homes
are a necessary appliance. With a computer available at home, students
obtain tutorial assistance from software and on line resources without waiting
for a parent's availability or having to travel to a distant library.
Just like in classrooms, home study computer use requires
that the student have proper room lighting, supporting seat and a keyboard and
monitor adjusted to the correct positions. Without these adjustments, learning
productivity drops, potential injury results and, it is simply uncomfortable.
- To work well, a home use student's workstation has to combine form,
quality and function in minimal space.
- It must provide an attractive, comfortable task area suitable for long
hours of studying.
- There must be space for books, drawing, hand writing and more.
- It must be secure.
- It has to be organized.
- The student's computer study area must be an attractive part of home
decor; compatible with total home space use.
- Computer furniture must enhance its users productivity.
Home student use of computers
is not a luxury.
Top - Page Index
In class room, computer laboratory and library
Suitable for fixed hard-wired networks, wireless networks
or stand-alone applications, Learning Stations™
position in a variety of configurations to enhance
teaching. For wireless and stand-alone applications,
mobility permits locating and relocating into study groups with minimal disruption.
Teacher desk units are available with special storage and
security features including server security, file and record storage.
Special application configurations
include engineering, graphics and GIS workstation layouts to take into account
use of digitizers, large monitors (21") and specialized communication equipment.
Dual station units are designed for student and trainer to work side by side.
Top - Page Index
Computer Labs and Networking
Grouping computers into a centralized "computer lab"
initially costs less; but research and experience have shown that because of
limitations on student computer-use, is less educationally effective than having
individual computers for individual students in their own classroom.
Costs for interconnecting ("hard-wiring")
classrooms on a retrofit basis have proved to be high and require technicians
to accomplish the sometimes complex fitting of cables within existing structures.
Changes are difficult and most maintenance problems with networks are the result
of cabling problems. It all has to do with technological development and willingness
of corporate America to support education.Top
- Page Index
The Summerland Student Learning Program
| A few years ago in Japan, the government mandated that Saki be drunk at
official functions instead of imported champagne. The objective was to
use what is available instead of what is scarce (and expensive),
and, to "inspirit" the Saki industry along the way. |
Approached in this way, we studied needs, technologies and
alternatives/options that could maximize effectiveness of educational uses for
computers and, for our brand's development. We examined student computer use
to determine habits, practices and attitudes of computer-using student, teachers
and administrators. We listened to parents, their children and educators.
We learned how critical school cost factors were - - and, discovered a
way to assist school personnel and faculty to rapidly implement an affordable
practical program.
Analysis of student use of computers, interviews and tests
of a broad range of potential solutions yielded data from which we developed
designs. We prototyped, and tested. We added what we had learned in development
of The OFFICEtm monitor concealment and lift and roll units. The result is an
important product solution for education. Top
- Page Index
The Summerland Plan
Technology advances have displaced hundreds of thousands
of older computers; they have been obsoleted by faster, more powerful models.
Many older PCs aren't capable of using Windows 95 and many more are modem less
- - not able to cope with the requirements for Internet access. Their principal
virtue is that they are readily available as they are replaced in company systems
by up-to-date, more powerful models.
We found a method for schools to obtain and use these computers
- - adapting them at low cost to meet needs of tomorrow's school classroom.
It involves using donated "old" computers as student terminals connected
to an in-classroom central computer (server) that CAN run Windows 95,
its myriad software programs, and provide access to the Internet.
The goal, at minimum (and affordable) cost, is to
provide every student with a networked terminal at their desk. To make this
possible in the near term, technical support, maintenance and access to continuing
upgrades are defined plan components. Protocols to use retrofitted "old"
computers in the teaching environment offer at lower cost, a flexible
solution. Top - Page Index
Here's how it works:
A school district implemented computer-obtaining program
includes establishing working relationships with local industry, business, academia
and government to find suitable numbers of usable technology-displaced computers,
monitors and cabling.
The next step of the hardware acquisition protocol is arranging
for computer manufacturer and/or computer owners to provide assistance in hardware
appraisal, repairs and clean-up. Installation and maintenance assistance from
corporate I.S. staffs, volunteers and supporting organizations is negotiated.
Low cost computers and monitors (286 - 386 - 486)
systems are modified to use a specialized system architecture that lets students
run Windows applications using any computer over any connectivity at full LAN
speeds. It permits the "old" computers to function just as though
they had the capabilities of the server to which they are interconnected.
1. Before use, each of the donated "old" computers is "performance-checked"
to validate operational components; then, a modest amount of memory (4 MB) installed
to create a working area within the computer in which a new system software
architecture functions. If not already present, a network capability "card"
is added.
2. Retrofitted computers are placed in the classroom. They are interconnected
to a classroom server holding specialized teaching software and data storage
(each student has their own "storage space" for their work).
Wireless Networking
One way to make a computer classroom network Project even
more "special" is that it can function without hard-wired network
cabling - - Each retrofitted "old" computer becomes a combination
transmitter and receiver - - sending signals to a server and receiving data
back - - at rates and in numbers that, for example make it possible for every
student in every elementary school class to simultaneously be working on their
computers - - all at the same time - - each on different projects, using different
software programs; even accessing different parts of the Internet. The
"wireless" system uses a wireless server so the only in-class wiring
is limited to 110v power for the students' computer/monitor.
With a Student Learning Station equipped wireless
system, the only classroom wiring needed is for electrical power for each Learning
Station. With wireless networks, it is easy to move students and their computers
within a classroom to fit student and teaching requirements.
Wireless Network Technologies
Wireless network systems fall into three main categories,
Radio, Direct infra-red and Diffuse infra-red. Each type of system offers advantages
and disadvantages over the others. Wireless networks are now considered as a
viable, cost effective alternative to running conventional network cabling.
The following summarizes the alternatives (options) available.
Radio Technology
Radio technology is by for the most prolific technology in the wireless LAN
market. Radio is also the most flexible and most costly of all the wireless
technology. Radio networks allow users to freely roam about a building without
loss of signal. When compared to infra-red, the trade off for this freedom is
lower data rate, The data rate in most wireless radio equipment is in the region
of 1.6 Mbps which is lower than infrared but sufficient for most LAN applications.
In the past, using radio waves for communication in the
computer industry was been hindered by the need for costly licenses for radio
bandwidth. This problem has been addressed with the introduction of the ISM
bands (Industrial, Scientific and Medical) which operates in the vicinity of
2.4 GHz. This enables radio transmitters to broadcast network data over
small areas such as a school district.
Infrared Technology
Infrared is simply "invisible" light. Infrared
has almost all the physical properties of visible light with the most notable
exception being that our eyes cannot "see" it. These high-frequency
light waves are lower frequency in the electromagnetic spectrum than visible
light. Infrared will not go through walls; however, it will pass through open
doorways, reflect off walls and bounce around corners just like sunlight and
office lighting.
Advantages of Infrared (IR)
- 1. Total power consumption for infrared is low.
2. IR does not interfere with other communications, nor is it susceptible
to EMI or RF.
3. Since infrared signals don't penetrate walls, signals cannot escape to
the outside to cause interference with other classrooms.
4. The infrared spectrum is unregulated globally, which allows for any infrared
system design to be used anywhere in the world .
5. The biological effects of infrared are well understood. There is a laser
safety standard for eye exposure to coherent infrared laser communications;
however, at the low levels used in directed and diffuse, most products emit
less infrared than a standard light bulb.
There are two types of infrared network transmission systems.
1. Directed (line-of-sight) or (point-and-shoot)
2. Diffuse (fill service or coverage area like an non-shaded light bulb)
Directed Infra-red characteristics:
1. Coherently focused (infrared laser)
2. Narrow field-of-view (similar to a flashlight)
Direct infra-red signals need a clear line of sight.
The most familiar "point-and-shoot" example is the TV remote control
followed closely with the point-to-point link for file transfers from a PC to
peripheral devices, such as a printer. Directed infrared transmission offers
convenient, inexpensive, and reliable wireless connection.
Some computers have infrared ports. For them, the
only other piece of hardware needed for networking is an infra-red sensor which
connects that computer to the network. These commercially available access points
can be liberally spread around an area for example: on desks and benches, creating
the wireless network.
Users then are connected directly to a hard-wired network
without the need for cables. Direct infrared sensor retail costs are relatively
low (about one-half the cost of a radio network computer card) and do
not require the RF access-point which costs approximately three times the cost
of the RF cards.
Drawbacks of Directed infra-red are:
1. Lack of speed. In order to be useful as a replacement to traditional
methods of connecting to the network the infra-red link would have to perform
at 4Mb/s. All "old" computers and most of the current ones can not
support data transfer at this standard. They achieve only 115Kb/s.
2. Less Flexible than other alternatives. Direct infrared is
line-of-site. It is less flexible than RF when it comes to freedom of movement.
Despite these difficulties, Direct infra-red technology is a very useful solution
to be considered for user-friendly connection of a computer to a network.
Difuse Infra-red Technology
Diffuse infra-red technology works by flooding an area
with infra-red light, much the same way a conventional light bulb illuminates
a room. The infra-red signal bounces of the walls and ceiling so that a receiver
can get the signal regardless of orientation. Diffuse infra-red technology
is a compromise between direct infra-red and radio technology. It combines the
advantages of high data rates from infra-red and the freedom of movement from
radio.
However, it also inherits some disadvantages. Although
it transmits at 4Mbits/s (twice that of current radio systems), this transfer
rate must be shared among all users, unlike directed infra-red. And unlike direct
infra-red, although a user can roam around freely within a room, the user is
still confined to individual rooms unlike radio signals which can pass through
walls. Radio unlike diffuse infra-red can use one access point to cover several
rooms, possibly even an entire building. Diffused infra-red requires one,
(possibly more), access points per room. The diffused IR system uses globe antennas
mounted on walls or in the ceiling to communicate with receivers which connect
to student computers. Top - Page
Index
The Summerland strategic plan is to create an integrated, detailed
specification, logistics and contract management program melded in an overall
Master Program Specification - - one
which is readily able to be self-implemented by individual school districts.
Program Specification
The Master Program Specification is designed to be able
to be executed by local vendors/contractors. For maintenance of the highest
standards of performance and quality, all phases of tasks are performed in accordance
with the Specification under contract from the school district/superintendent.
Program protocols include:
- Development and oversight of "sources" for "old" computers,
including mechanics for testing and upgrading.
- Installation agreements for set-up, testing and performance validation.
- On-site (local) maintenance contracts defining requirements, performance
standards and cost.
- Coordination methods for working with Federal, state and local agencies
are quantified in order that schools are able to take advantage of available
grant and aid funding sources to maximize the number of computers per classroom.
Fundamental questions to be considered include:
- · How cost effective is locating, testing and modifying otherwise not-useable
computer systems to achieve new-equipment reliability levels vs. alternatives
?
- · How many of these computer systems can be made available by local,
state and regional sources?
- · What computer architecture will best provide the functionality desired
for the class needs?
- · What software (educational) should be on the server?
- · How cost effective are wireless networks when compared to traditional
wired systems for school needs?
- · What problems may be expected in the conversion of "old"
computers, use of special computer architectures, installation and maintenance
of the wireless system?
- · How well will wireless communication stand up to the demands of classroom
use?
- · How readily expandable is the developed system to meet the balance
of School needs?
Project Direction
The general direction for each iteration of the project
involves analyzing the target school's student, teaching and administrative
requirements/ needs in concert with:
- Integrating computer network technology currently available and that being
developed for near-future release
- Developing and refining protocols to acquire and make computers usable
- Developing sustainable support services.
- Selecting the most economic combination/option which best-fits the aims
of the project.
The next step
Once initial planning is completed and prototype demonstrations
have proved satisfactory, (and adequate numbers of suitable, adaptable, computers
are obtained), best-fit technology and server-based system selection is
performed; a demonstration network design will be implemented in an initial
classroom in the school. Testing of performance and utility will validate functionality
of the combination of computers and network. Results will be published and disseminated
as part of the 'Program Master Specification" for adoption by other schools.
Early program milestone evaluations determine the practicality
of system expansion feasibility:
- (1) Incorporating the system in all classes
(2) Practicality of expansion to include middle and high-school classrooms
and administrative requirements
(3) Consideration of expansion of wireless capabilities to encompass
multiple schools within the school district so as to create a teaching (90%)
and administrative (10%) operational network. Top
- Page Index
Five part Phased Plan
For evaluation, the Project has been broken down into the different phases
the project will go through as well as defining administrative tasks that need
to be performed.
1. INITIAL PROJECT PLANNING
- Formation of a Project Steering Group. The Project Steering
Group is to be formed to advise and make key decisions about the project,
such as which wireless system to use. The Steering Group will include representation
from school administration, educators and parent representatives in addition
to technical personnel and the Program Monitor.
- Detailed Project Proposal Document Development A step-by-step detailed
schedule for all project elements is developed under direction of the Project
Steering Group. A PDU outline is to define all procurement, implementation
and installation protocols including training of teaching staff in system
use and maintenance.
- Decision on classrooms to be included in the system. Decide
which are to be included in the final system.
- Initial contact with regional sources for computers for retrofitting.
Computer manufacturers, government agency and private industry assistance
will be solicited.
- Initial contact with wireless network suppliers. Details of technical
specifications, performance analysis information and evaluation equipment,
will be developed; forming close industrial relations with suppliers for on-going
assistance.
2. SELECTION OF WIRELESS NETWORKING TECHNOLOGY
- A detailed comparison is made of the different manufacturers' available
applied technology in order to select the best system for the individual school.
- Final decision of system to be adopted. The final decision
of the wireless technology and the supplier to be used will be taken by the
Project Steering Group after a detailed presentation of the results of the
studies made.
- Production of an interim report. The interim report will detail
the studies and tests performed and the reasons for reaching the decision
on which technology to use.
3. DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF FINAL SYSTEM
- Design of the system. Once network technology has been
chosen, the final design can be drafted and evaluated as to how each student
can connect/interact/ use the server system.
- Implementation of a demonstration design system. A prototype demonstration
including each step from physical retrofit of "old" computers to
set-up and operation of an operating server/client demonstration (two computer
stations) will be made for presentation to a Project Steering Group selected
audience.
- Installation of network statistic analysis software. In order
to analyze the performance of the finished system, a package will be used
to test features such as average data rate, reliability of the connection
etc..
- Initial test of the system. A single classroom will be partially
computer-equipped (between one-third and one-half of all students in the selected
class will be computer equipped). This will test initial system installation
and operation and impact on classroom/students/teachers.
4. EVALUATION OF DEMONSTRATION SYSTEM
- Detailed analysis of the data gained from the initial system test.
- Interviews with the users taking part in the evaluation. Students
and teachers will evaluate the program and system operation. Additional experts
from Universities and industry will be selected by the project steering
group to obtain external assessment of results achieved. This, along
with analysis of the network data, will form the bulk of the data used to
determine the success of the project and feasibility of adoption for the entire
school and for its extendibility to other schools and school districts.
- Testing Result Comparisons
- Measurement of student learning will be performed. Regular Princeton
test results for the computer-equipped class will be compared to test scores
from like grade classes in non-computer equipped classes within the same school
district. Score variances will be evaluated to establish degrees of differences.
5. DOCUMENTATION AND DISSEMINATION OF RESULTS
- Production of a WWW site dedicated to the project.
- Interim reports to be submitted at key stages in the project.
- Report of final results from the project.
- Organization of a regional conference/meeting to disseminate the
results. Top - Page Index
Action steps and 20 week time-table
Tentative Functional Scheduling - - Based on a single school within a District.
Weeks 1 - 3
The school will provide basic data e.g. # rooms, measurements (room dimensions),
construction data, number students, desired software (teaching software), curriculum
planning and related issues including permitting and other authorization requirements.
Weeks 4 - 6
From the preliminary data, server design will be accomplished by Summerland.
This will define hard-disk space requirements, performance (speed) and other
operational parameters. Following server design, system parameters will be quantified
and network parameters established. Cost estimates will be developed for all
procurement items and service applications. Costs will be validated after review
by the Project Steering Group.
Week 7
A detailed cost summary will be prepared for an initial oral presentation
to be made by the Project Steering Group to cognizant representatives of state
and federal agencies, school district and parents. From this summary a full-system
performance contract for the scope of work agreed-upon between Summerland and
the District will be executed.
Week 8
A presentation incorporating input from the initial presentation and feedback
will be prepared for both oral and written public informational dissemination
presentation to transfer information and to elicit additional requirements.
Weeks 9 - 12
Development of detailed procedures completed, funding quantified and task
contracts prepared and negotiated.
Week 13
Project Implementation Start
Week 20
First Phase Completed
Top - Page Index
The OFFICE™









